Parity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the parity of an object states whether it is even or odd.
This concept begins with integers. An even number is an integer that is "evenly divisible" by 2, i.e., divisible by 2 without remainder; an odd number is an integer that is not evenly divisible by 2. (The old-fashioned term "evenly divisible" is now almost always shortened to "divisible".) A formal definition of an even number is that it is an integer of the form n = 2k, where k is an integer; it can then be shown that an odd number is an integer of the form n = 2k + 1.
Examples of even numbers are −4, 8, and 1728. Examples of odd numbers are −5, 9, 3, and 71. This classification only applies to integers, i.e., a fractional number like 1/2 or 4.201 is neither even nor odd.
The sets of even and odd numbers can be defined as following:
- Even =
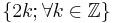
- Odd =
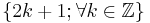
A number (i.e., integer) expressed in the decimal numeral system is even or odd according to whether its last digit is even or odd. That is, if the last digit is 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9, then it's odd; otherwise it's even. The same idea will work using any even base. In particular, a number expressed in the binary numeral system is odd if its last digit is 1 and even if its last digit is 0. In an odd base, the number is even according to the sum of its digits – it is even if and only if the sum of its digits is even.
Contents |
Arithmetic on even and odd numbers
The following laws can be verified using the properties of divisibility. They are a special case of rules in modular arithmetic, and are commonly used to check if an equality is likely to be correct by testing the parity of each side. As with ordinary arithmetic, multiplication and addition are commutative and associative, and multiplication is distributive over addition. However, subtraction in parity is identical to addition, so subtraction also possesses these properties (which are absent from ordinary arithmetic).
Addition and subtraction
- odd ± even = odd;
Rules analogous to these for divisibility by 9 are used in the method of casting out nines.
Multiplication
- even × even = even;
- even × odd = even;
- odd × odd = odd.
Division
The division of two whole numbers does not necessarily result in a whole number. For example, 1 divided by 4 equals 1/4, which is neither even nor odd, since the concepts even and odd apply only to integers. But when the quotient is an integer, it will be even if and only if the dividend has more factors of two than the divisor.
History
The ancient Greeks considered 1 to be neither fully odd nor fully even. Some of this sentiment survived into the 19th century: Friedrich Wilhelm August Fröbel's 1826 The Education of Man instructs the teacher to drill students with the claim that 1 is neither even nor odd, to which Fröbel attaches the philosophical afterthought,
It is well to direct the pupil's attention here at once to a great far-reaching law of nature and of thought. It is this, that between two relatively different things or ideas there stands always a third, in a sort of balance, seeming to unite the two. Thus, there is here between odd and even numbers one number (one) which is neither of the two. Similarly, in form, the right angle stands between the acute and obtuse angles; and in language, the semi-vowels or aspirants between the mutes and vowels. A thoughtful teacher and a pupil taught to think for himself can scarcely help noticing this and other important laws.
Music theory
In wind instruments with a cylindrical bore and in effect closed at one end, such as the clarinet at the mouthpiece, the harmonics produced are odd multiples of the fundamental frequency. (With cylindrical pipes open at both ends, used for example in some organ stops such as the open diapason, the harmonics are even multiples of the same frequency for the given bore length, but this has the effect of the fundamental frequency being doubled and all multiples of this fundamental frequency being produced.) See harmonic series (music).
Higher mathematics
The even numbers form an ideal in the ring of integers, but the odd numbers do not — this is clear from the fact that the identity element for addition, zero, is an element of the even numbers only. An integer is even if it is congruent to 0 modulo this ideal, in other words if it is congruent to 0 modulo 2, and odd if it is congruent to 1 modulo 2.
All prime numbers are odd, with one exception: the prime number 2. All known perfect numbers are even; it is unknown whether any odd perfect numbers exist.
The squares of all even numbers are even, and the squares of all odd numbers are odd. Since an even number can be expressed as 2x, (2x)2 = 4x2 which is even. Since an odd number can be expressed as 2x + 1, (2x + 1)2 = 4x2 + 4x + 1. 4x2 and 4x are even, which means that 4x2 + 4x + 1 is odd (since even + odd = odd).
Goldbach's conjecture states that every even integer greater than 2 can be represented as a sum of two prime numbers. Modern computer calculations have shown this conjecture to be true for integers up to at least 4 × 1014, but still no general proof has been found.
The Feit–Thompson theorem states that a finite group is always solvable if its order is an odd number. This is an example of odd numbers playing a role in an advanced mathematical theorem where the method of application of the simple hypothesis of "odd order" is far from obvious.
Parity for other objects
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 | 8 | ||||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h |
Parity is also used to refer to a number of other properties.
- The parity of a permutation (as defined in abstract algebra) is the parity of the number of transpositions into which the permutation can be decomposed. For example (ABC) to (BCA) is even because it can be done by swapping A and B then C and A (two transpositions). It can be shown that no permutation can be decomposed both in an even and in an odd number of transpositions. Hence the above is a suitable definition. In Rubik's Cube, Megaminx, and other twisty puzzles, the moves of the puzzle allow only even permutations of the puzzle pieces, so parity is important in understanding the configuration space of these puzzles.
- The parity of a function describes how its values change when its arguments are exchanged with their negations. An even function, such as an even power of a variable, gives the same result for any argument as for its negation. An odd function, such as an odd power of a variable, gives for any argument the negation of its result when given the negation of that argument. It is possible for a function to be neither odd nor even, and for the case f(x) = 0, to be both odd and even.
- Integer coordinates of points in Euclidean spaces of two or more dimensions also have a parity, usually defined as the parity of the sum of the coordinates. For instance, the checkerboard lattice contains all integer points of even parity. This feature manifests itself in chess, as bishops are constrained to squares of the same parity; knights alternate parity between moves. This form of parity was famously used to solve the Mutilated chessboard problem.